4A0-100 Exam Dumps - Nokia IP Networksand Services Fundamentals
Searching for workable clues to ace the Nokia 4A0-100 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s 4A0-100 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
Which of the following enables service providers to support multiple customers with the same VLAN ID over the same backbone?
Which of the following statements about the system interface on the Nokia 7750 SR is FALSE?
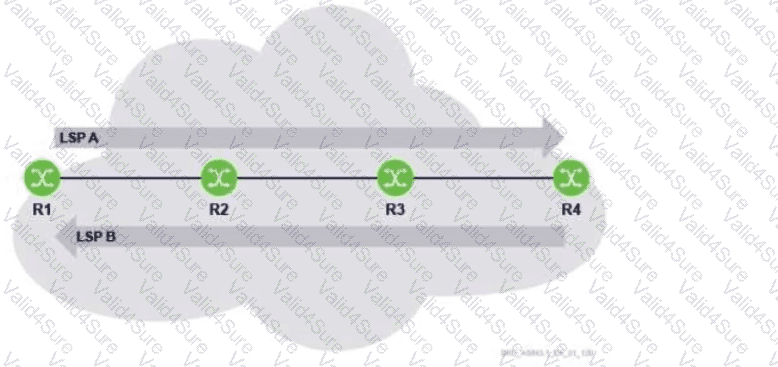
Which of the MPLS routers is responsible for pushing new labels for LSP A and LSP B?
What is the sequence of messages that must be exchanged between a DHCP client and a server for the client to receive an IP address?