CCRA-L2 Exam Dumps - Certified Credit Research Analyst Level 2
The following information pertains to bonds:
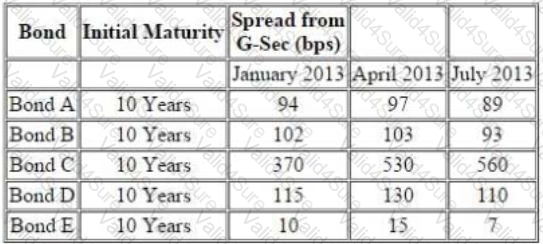
Further following information is available about a particular bond ‘Bond F’
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 2.25% year(s) its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds to YTM of 9.22%. The following are the benchmark YTMs.
Assuming the G-Sec has not changed from the time January 2013 to April 2013, what can you predict about the changes bond price and change in issues borrowing rates:
In an industry there are only 20 firms and each of them has equal share. Compute Herfindahl Hirschman Index
and state the level of concentration in the industry.
For considering the assignment of probabilities, which of the following aspects are taken into account?
The following information pertains to bonds:
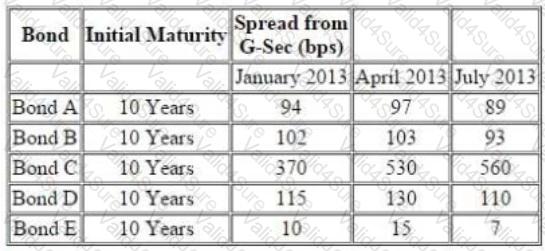
Further following information is available about a particular bond ‘Bond F’
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 2.25% year(s) its current price is INR105.31, which ccorresponds to YTM of 9.22%. The following are the benchmark YTMs.
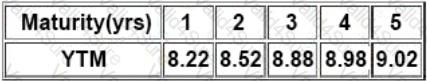
Assume that the general market rates have increased. An issuer, Revolution Ltd has plans to roll over its existing commercial paper and forth coming reset dates for its floating rate bonds are very near. Which of the following ratios for revolution will get impacted?
Awesome Mobile Ltd is a leading mobile seller who manufactures mobile phone under own brand Awesome.
Which of the following is the biggest business risk for Awesome?