- Home
- Isaca
- Isaca Certification
- CRISC - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control
CRISC Exam Dumps - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control
An internally developed payroll application leverages Platform as a Service (PaaS) infrastructure from the cloud. Who owns the related data confidentiality risk?
IT infrastructure head
Human resources head
Supplier management head
Application development head
Answer:
Explanation:
Data confidentiality risk is the risk that the data may be accessed, disclosed, or modified by unauthorized parties, resulting in breaches of privacy, trust, or compliance1. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, without requiring the users to manage the underlying infrastructure2. An internally developed payroll application is an application that is created and maintained by the organization itself, rather than by a third-party vendor, and that is used to process and manage the payroll data of the organization’s employees3. The owner of the data confidentiality risk is the person or entity that has the authority and accountability for the data and its protection, and that is responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risk. The owner of the data confidentiality risk related to an internally developed payroll application that leverages PaaS infrastructure from the cloud is the human resources head, as they are the person who oversees the human resources function and the payroll data of the organization. The human resources head has the best understanding of the sensitivity, value, and usage of the payroll data, and the potential impacts and implications of a data confidentiality breach. The human resources head also has the ability and responsibility to define and implement the policies, procedures, and controls that are necessary to protect the payroll data, and to monitor and report on the performance and compliance of the data confidentiality risk management. The IT infrastructure head, the supplier management head, and the application development head are not the best choices for owning the data confidentiality risk related to an internally developed payroll application that leverages PaaS infrastructure from the cloud, as they do not have the same level of authority and accountability as the human resources head. The IT infrastructure head is the person who oversees the IT infrastructure function and the PaaS infrastructure of the organization. The IT infrastructure head may be involved in providing input and feedback to the human resources head on the data confidentiality risk management, especially those related to the PaaS infrastructure, but they do not have the final say or the overall responsibility for the payroll data and its protection. The supplier management head is the person who oversees the supplier management function and the relationship with the cloud service provider that provides the PaaS infrastructure. The supplier management head may be involved in negotiating and enforcing the service level agreements and the security requirements with the cloud service provider, but they do not have the authority or the expertise to manage the data confidentiality risk of the payroll data. The application development head is the person who oversees the application development function and the development, testing, and deployment of the payroll application. The application development head may be involved in designing and implementing the security features and controls of the payroll application, but they do not have the perspective or the influence to manage the data confidentiality risk of the payroll data. References = 3: Payroll Software: What Is It & How Does It Work? | QuickBooks2: What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)? | IBM1: Data Confidentiality: Identifyingand Protecting Assets Against Data … : [Risk Ownership - Risk Management] : [Human Resources and Payroll Security Policy - University of …] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.1: IT Risk Concepts, pp. 17-19.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.1: Risk Identification, pp. 57-59.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: Risk Monitoring, pp. 189-191.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.1: Control Design, pp. 233-235.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.2: Control Implementation, pp. 243-245.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.3: Control Monitoring and Maintenance, pp. 251-253.]
What can be determined from the risk scenario chart?
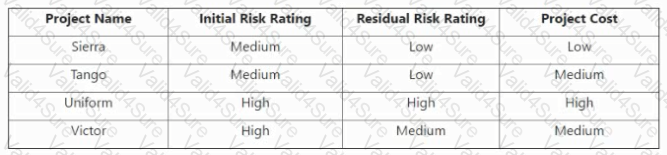
Relative positions on the risk map
Risk treatment options
Capability of enterprise to implement
The multiple risk factors addressed by a chosen response
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk scenario chart shows the initial and residual risk ratings, and the project cost, for four projects named Sierra, Tango, Uniform, and Victor. The initial risk rating is the level of risk before applying any controls or mitigation measures, while the residual risk rating is the level of risk after applying the controls or measures. The project cost is the amount of resources required to implement the project. These three factors can be used to determine the relative positions of the projects on a risk map, which is a graphical tool for displaying the risks based on their impact and likelihood. The risk map can help to prioritize and compare the risks, and to select the most appropriate risk response strategy. The other options are not the best answers, as they are not directly shown or derived from the risk scenario chart. The risk treatment options are the possible actions that can be taken to address the risks, such as accept, avoid, mitigate, or transfer. The capability of enterprise to implement is the ability of the organization to execute the risk response plan,considering the available resources, skills, and constraints. The multiple risk factors addressed by a chosen response are the various elements that contribute to or affect the risk, such as the threat sources, events, vulnerabilities, assets, and impacts. These factors are not explicitly stated or measured in the risk scenario chart, and may require further analysis or information. References = How to Write Strong Risk Scenarios and Statements - ISACA; Identifying the Right Risk Scenarios to Measure with FAIR; How to write good risk scenarios and statements
To help ensure all applicable risk scenarios are incorporated into the risk register, it is MOST important to review the:
risk mitigation approach
cost-benefit analysis.
risk assessment results.
vulnerability assessment results
Answer:
Explanation:
To help ensure all applicable risk scenarios are incorporated into the risk register, it is most important to review the risk assessment results, which are the outputs of the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks that affect a project or an organization. The risk assessment results provide information on the sources, causes, impacts, likelihood, and severity of the risks, as well as the existing controls and their effectiveness. The risk assessment results help to determine the risk level and priority of each risk scenario, and to select the most appropriate risk response strategy. The risk assessment results are the basis for creating and updating the risk register, which is a document that records and tracks theidentified risks, their characteristics, responses, owners, and status12. The other options are not the most important factors to review, as they are either derived from or dependent on the risk assessment results. The risk mitigation approach is the plan and actions to reduce the impact or likelihood of the risks, and it is based on the risk assessment results. The cost-benefit analysis is the comparison of the costs and benefits of implementing the risk response strategy, and it is influenced by the risk assessment results. The vulnerability assessment results are the identification and measurement of the weaknesses or gaps in the information systems or resources, and they are part of the risk assessment results. References = Risk Assessment in Project Management | PMI; Risk Assessment Process: Definition, Steps, and Examples; Risk Assessment - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics; Risk Register: A Project Manager’s Guide with Examples [2023] • Asana; What Is a Risk Register? | Smartsheet
An application owner has specified the acceptable downtime in the event of an incident to be much lower than the actual time required for the response team to recover the application. Which of the following should be the NEXT course of action?
Invoke the disaster recovery plan during an incident.
Prepare a cost-benefit analysis of alternatives available
Implement redundant infrastructure for the application.
Reduce the recovery time by strengthening the response team.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the next course of action when there is a gap between the acceptable downtime and the actual recovery time of an application is to prepare a cost-benefit analysis of alternatives available to reduce the gap. The cost-benefit analysis should compare the costs of implementing different risk response options, such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer or acceptance, with the benefits of reducing the impact and likelihood of the risk. The cost-benefit analysis should also consider the alignment of the risk response options with the enterprise’s risk appetite, business objectives and strategy. The cost-benefit analysis should help the application owner and the risk owner to select the most appropriate risk response option that optimizes the value of the application and minimizes the residual risk.
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.2: Risk Response Process, pp. 162-1631
Which of the following BEST enables effective risk-based decision making?
Performing threat modeling to understand the threat landscape
Minimizing the number of risk scenarios for risk assessment
Aggregating risk scenarios across a key business unit
Ensuring the risk register is updated to reflect changes in risk factors
Answer:
Explanation:
Detailed Explanation:An updatedrisk registerensures that decision-makers have accurate, timely information about current risks, enabling informed, risk-based decisions that align with organizational priorities and changes in the environment.
Which of the following is the MOST cost-effective way to test a business continuity plan?
Conduct interviews with key stakeholders.
Conduct a tabletop exercise.
Conduct a disaster recovery exercise.
Conduct a full functional exercise.
Answer:
Explanation:
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a document that describes the procedures and actions that an organization will take to ensure the continuity of its critical functions and operations in the event of a disruption or disaster12.
Testing a business continuity plan is a method of evaluating the effectiveness and readiness of the BCP, and identifying and addressing any gaps or weaknesses in the plan34.
The most cost-effective way to test a business continuity plan is to conduct a tabletop exercise, which is a type of simulation that involves gathering the key stakeholders and participants of the BCP, and discussing and reviewing the roles, responsibilities, and actions that they will take in response to a hypothetical scenario of a disruption or disaster56.
A tabletop exercise is the most cost-effective way because it requires minimal resources and time, and can be conducted in a regular meeting room or online platform56.
A tabletop exercise is also the most cost-effective way because it provides a high-level overview and assessment of the BCP, and can identify and address the major issues or challenges that may arise in the implementation of the plan56.
The other options are not the most cost-effective ways, but rather possible alternatives or supplements that may have different levels of complexity or cost. For example:
Conducting interviews with key stakeholders is a way of testing a business continuity plan that involves asking and answering questions about the BCP, and collecting feedback and suggestions from the people who are involved or affected by the plan78. However, this way is not the most cost-effective because it may not cover all the aspects or scenarios of the BCP, and may not facilitate the interaction or collaboration among the stakeholders78.
Conducting a disaster recovery exercise is a way of testing a business continuity plan that involves activating and executing the BCP in a realistic and controlled environment, and measuring the outcomes and impacts of the plan . However, this way is not the most cost-effective because it requires a lot of resources and time, and may disrupt or interfere with the normal operations of the organization .
Conducting a full functional exercise is a way of testing a business continuity plan that involves simulating and testing the BCP in a live and dynamic environment, and involving the external entities and stakeholders that are part of the plan . However, this way is not the most cost-effective because it requires the most resources and time, and may pose the highest risk or challenge to the organization . References =
1: Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Definition1
2: Business Continuity Planning - Ready.gov2
3: Testing, testing: how to test your business continuity plan4
4: Comprehensive Guide to Business Continuity Testing | Agility5
5: How to Conduct a Tabletop Exercise for Business Continuity3
6: Tabletop Exercises: A Guide to Success6
7: How to Conduct Testing of a Business Continuity Plan7
8: Business Continuity Plan Testing: Interviewing Techniques8
Disaster Recovery Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Disaster Recovery Testing Scenarios: A Guide to Success
Functional Exercises: A Guide to Success
Functional Exercise Toolkit
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when developing an organization's risk taxonomy?
Leading industry frameworks
Business context
Regulatory requirements
IT strategy
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk taxonomy is a classification or categorization system that defines and organizes the risks that may affect the organization’s objectives and operations. It includes the risk domains, categories, subcategories, elements, attributes, etc., and the relationships and dependencies among them. A risk taxonomy can help the organization to identify, analyze, evaluate, and communicate the risks, and to align them with the organization’s strategy and culture.
The most important consideration when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy is the business context, which is the set of internal and external factors and conditions that influence and shape the organization’s objectives, operations, and performance. It includes the organization’s vision, mission, values, goals, stakeholders, resources, capabilities, processes, systems, etc., as well as the market, industry, regulatory, social, environmental, etc., factors and conditions that affect the organization.
Considering the business context when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy ensures that the risk taxonomy is relevant, appropriate, and proportional to the organization’s needs and expectations, and that it supports the organization’s objectives and values. It also helps to ensure that the risk taxonomy is consistent and compatible with the organization’s governance, risk management, and control functions, and that it reflects the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance.
The other options are not the most important considerations when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy, because they do not address the fundamental question of whether the risk taxonomy is suitable and acceptable for the organization.
Leading industry frameworks are the established or recognized models or standards that provide the principles, guidelines, and best practices for the organization’s governance, risk management, and control functions. Leading industry frameworks can provide useful references and benchmarks when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy, but they are not the most important consideration, because they may not be specific or applicable to the organization’s business context, and they may not reflect the organization’s objectives and values.
Regulatory requirements are the rules or obligations that the organization must comply with, as imposed or enforced by the relevant authorities or regulators. Regulatory requirements can provide important inputs and constraints when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy, but they are not the most important consideration, because they may not be comprehensive or sufficient for the organization’s business context, and they may not support the organization’s objectives and values.
IT strategy is the plan or direction that the organization follows to achieve its IT objectives and to align its IT resources and capabilities with its business objectives and needs. IT strategy can provide important inputs and alignment when developing an organization’s risk taxonomy, but it is not the most important consideration, because it may not cover all the relevant or significant risks that may affect the organization’s business context, and it may not reflect the organization’s objectives and values. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 175
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is the MOST useful indicator to measure the efficiency of an identity and access management process?
Number of tickets for provisioning new accounts
Average time to provision user accounts
Password reset volume per month
Average account lockout time
Answer:
Explanation:
The average time to provision user accounts is the most useful indicator to measure the efficiency of an identity and access management (IAM) process, because it reflects how quickly and smoothly the process can grant access to the appropriate users. The average time to provision user accounts can be calculated by dividing the total time spent on provisioning user accounts by the number of user accounts provisioned in a given period. A lower average time indicates a more efficient IAM process, as it means that users can access the resources they need without unnecessary delays or errors. A higher average time may indicate problems or bottlenecks in the IAM process, such as manual steps, complex workflows, lack of automation, or insufficient resources. The average time to provision user accounts can also be compared across different applications, systems, or business units to identify areas for improvement or best practices. The other options are less useful indicators to measure the efficiency of an IAM process. The number of tickets for provisioning new accounts shows the demand for the IAM process, but not how well the process meets the demand. The password reset volume per month shows the frequency of password-related issues, but not how effectively the IAM process handles them. The average account lockout time shows the impact of account lockouts on user productivity, but not how efficiently the IAM process prevents or resolves them. References = Top Identity and Access Management MetricsÂ