- Home
- CIPS
- CIPS Level 6 Professional Diploma in Procurement and Supply
- L6M2 - Global Commercial Strategy
L6M2 Exam Dumps - Global Commercial Strategy
Discuss the role and influence of industry regulators and international bodies in the business environment.
Answer:
Explanation:
The Role and Influence of Industry Regulators and International Bodies in the Business Environment
Introduction
Industry regulators and international bodies play acritical role in shaping the business environmentby enforcing regulations, setting industry standards, and ensuring fair competition. These organizations influence how businesses operate, impacting areas such astrade, finance, environmental sustainability, labor practices, and consumer protection.
Companies must comply with regulations set by bothdomestic industry regulatorsandglobal institutionsto maintain legal and ethical business operations.
1. Role of Industry Regulators
Industry regulators aregovernment-appointed or independent organizationsthat oversee specific sectors to ensure compliance with laws and standards. Their key functions include:
✅Enforcing Compliance– Ensuring companies adhere to legal requirements (e.g., financial reporting, safety regulations).✅Promoting Fair Competition– Preventing monopolies and anti-competitive practices.✅Consumer Protection– Safeguarding consumer rights and ensuring product/service quality.✅Regulating Market Entry and Operations– Setting standards for licensing, pricing, and ethical conduct.
💡Example of Industry Regulators
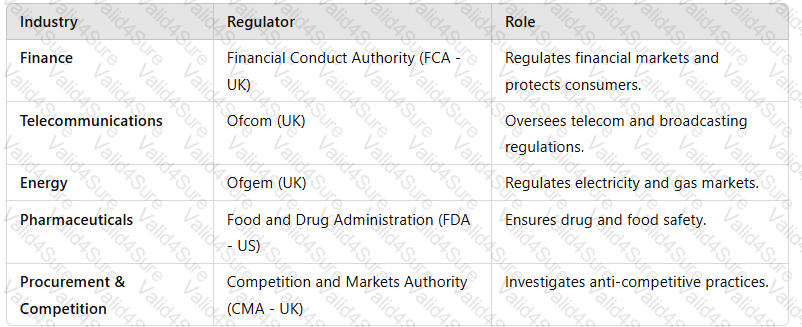 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Case Example:TheUK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA)blockedMicrosoft’s acquisition of Activision Blizzarddue to concerns over market dominance in cloud gaming.
2. Role of International Bodies
International bodies setglobal regulations, trade policies, and ethical standardsthat influence businesses operating across borders.
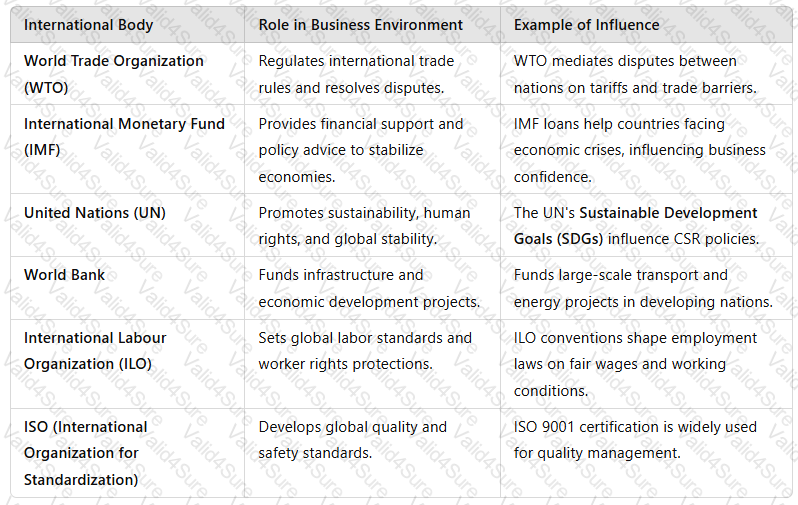 A table with text on it
Description automatically generated
A table with text on it
Description automatically generated
Case Example:TheWTO’s intervention in Brexit trade negotiationsaffected tariffs and supply chain costs for UK-based companies.
3. Influence of Industry Regulators and International Bodies on Business Strategy
Businesses must align their strategies with regulatory and international frameworks toensure compliance and avoid financial or reputational risks.
 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Example:TheEU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)forced global companies to enhancedata protection policiesor face heavy fines.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Regulatory and International Influence
✅Advantages
Promotes Stability & Fair Competition– Reduces market manipulation and corruption.
Protects Consumers & Employees– Ensures safety, fair wages, and ethical standards.
Encourages Innovation & Sustainability– Businesses invest in R&D to meet regulatory requirements.
Facilitates Global Trade– International trade agreements create business opportunities.
âŒDisadvantages
Regulatory Burdens & Compliance Costs– Strict laws increase operational costs.
Trade Barriers & Bureaucracy– Lengthy regulatory approval processes slow down market entry.
Risk of Overregulation– Too many rules can stifle competition and innovation.
💡Example:TheEU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)requires manufacturers topay for carbon emissions, increasing operational costs.
Conclusion
Industry regulators and international bodiesshape the business environmentby enforcing laws, ensuring ethical practices, and facilitating global trade. Companies must proactivelymonitor regulatory changes, integrate compliance into strategic planning, and adapt to international standardsto maintain market competitiveness and sustainability.
Describe 5 strategic decisions a company can make and how these decisions could impact upon competitive advantage.
Answer:
Explanation:
Five Strategic Decisions a Company Can Make and Their Impact on Competitive Advantage
Strategic decisions shape a company's direction and influence its long-term success. Below are five key strategic decisions and their impact oncompetitive advantage:
1. Market Entry Strategy
Decision:A company decides how to enter new markets (e.g., direct investment, joint ventures, exporting, franchising).
Impact on Competitive Advantage:✅Global Reach:Expanding into new markets increases revenue streams and reduces dependency on a single market.✅Risk Mitigation:Entering viajoint venturesoralliancescan reduce risks related to market unfamiliarity.✅Brand Positioning:Choosingpremium vs. cost-leadership entry strategiescan establish market dominance.âŒPotential Risk:Poor market research can lead to financial loss and reputational damage.
Example:Tesla entering China through direct investment inGigafactoriesto strengthen its supply chain and reduce production costs.
2. Supply Chain Strategy
Decision:Whether to adopt aglobalized, localized, or hybridsupply chain model.
Impact on Competitive Advantage:✅Cost Reduction:Strategic sourcing fromlow-cost countrieslowers production expenses.✅Resilience:Adiverse supplier basereduces risks of disruptions (e.g., geopolitical risks, pandemics).✅Speed to Market:Nearshoring strategies improve lead times and response to demand fluctuations.âŒPotential Risk:Over-reliance on global suppliers can lead to disruptions (e.g., semiconductor shortages).
Example:Apple’s dual sourcing strategy for chip manufacturing (Taiwan’s TSMC + US-based suppliers) improves resilience.
3. Innovation and R&D Investment
Decision:How much to invest inresearch and development (R&D)to drive product innovation.
Impact on Competitive Advantage:✅Differentiation:Unique and high-quality products create strong brand loyalty (e.g., iPhones, Tesla).✅First-Mover Advantage:Innovators set industry trends, making it difficult for competitors to catch up.✅Revenue Growth:New technologies create additional revenue streams (e.g., SaaS models in tech).âŒPotential Risk:High R&D costs with no guaranteed success (e.g., Google Glass failure).
Example:Pfizer and BioNTech’s rapid COVID-19 vaccine development, giving them first-mover advantage.
4. Pricing Strategy
Decision:Whether to compete oncost leadership, differentiation, or premium pricing.
Impact on Competitive Advantage:✅Market Penetration:Low-cost pricing attractsprice-sensitivecustomers (e.g., Walmart, Ryanair).✅Brand Exclusivity:Premium pricing enhances brand perception and profitability (e.g., Rolex, Louis Vuitton).✅Value-Based Pricing:Aligning price with perceived value increases customer retention.âŒPotential Risk:A race to the bottom in pricing wars can erode profit margins (e.g., budget airlines struggle with profitability).
Example:Apple uses apremium pricing strategywhile Xiaomi competes viacost leadershipin smartphones.
5. Digital Transformation Strategy
Decision:Investment inautomation, AI, and digital platformsto improve efficiency and customer engagement.
Impact on Competitive Advantage:✅Operational Efficiency:Automation reduces costs and increases productivity (e.g., Amazon’s AI-driven warehouses).✅Customer Experience:AI-driven personalization improves engagement (e.g., Netflix’s recommendation algorithms).✅Scalability:Digital platforms enable rapid global expansion (e.g., Shopify helping SMEs go digital).âŒPotential Risk:High initial investment with slow ROI; risk of cyber threats.
Example:Starbucks using AI-poweredpersonalization and mobile orderingto increase sales and customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Each strategic decision influences a company’s competitive positioning. The most successful companies alignmarket expansion, supply chain strategies, innovation, pricing, and digital transformationto create asustainable competitive advantage.
Discuss supply and demand factors in foreign exchange
Answer:
Explanation:
Supply and Demand Factors in Foreign Exchange
Introduction
Theforeign exchange (Forex) marketoperates on the fundamental principle ofsupply and demand, which determines currency values. Whendemand for a currency rises, its value appreciates, whilean oversupply causes depreciation.
Several factors influence thesupply and demandof foreign currencies, includinginterest rates, inflation, trade balances, investor sentiment, and geopolitical events.
This answer explores thekey supply and demand factors in Forex marketsand how they impact exchange rates.
1. Demand Factors in Foreign Exchange📈💰(What Increases Demand for a Currency?)
1.1 Interest Rate Differentials📊(Higher Interest Rates Attract Capital Inflows)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Investors seekhigher returns on savings and investments.
Higher interest ratesincrease demandfor the country’s currency.
💡Example:
When theUS Federal Reserve raises interest rates, theUS dollar (USD) strengthensas global investors buyUSD-denominated assets.
📌Key Takeaway:Countries withhigher interest rates attract more investors, increasing currency demand.
1.2 Inflation Rates📉(Low Inflation Strengthens Currency Demand)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Lower inflation preserves purchasing power, making the currency more attractive.
High inflationerodes currency value, reducing demand.
💡Example:
TheSwiss Franc (CHF) remains strongdue to Switzerland’slow inflation and economic stability.
In contrast,Turkey’s Lira (TRY) depreciateddue to high inflation, reducing investor confidence.
📌Key Takeaway:Stable inflation rates encourage demand for a currency, while high inflation weakens it.
1.3 Trade Balance & Current Account SurplusðŸŒ(Export-Led Demand for a Currency)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
Atrade surplus(exports > imports) increases demand for a country’s currency.
Foreign buyers need the country’s currency topay for goods and services.
💡Example:
China’s trade surplus increases demand for the Chinese Yuan (CNY)as global buyers purchase Chinese goods.
Germany’s strong exports strengthen the Euro (EUR)due to high international trade.
📌Key Takeaway:Exporting nations experiencehigher currency demand, boosting value.
1.4 Investor Confidence & Speculation📊(Market Sentiment Drives Demand)
✅Why It Affects Demand?
If investorsexpect a currency to appreciate, they buy more of it.
Safe-haven currencies seeincreased demand during global uncertainty.
💡Example:
Gold and the US Dollar (USD) strengthen during economic crises, as investors seek stability.
Brexit uncertainty weakened the British Pound (GBP)as investors speculated on UK economic instability.
📌Key Takeaway:Market psychology and speculation can drive short-term demand for a currency.
2. Supply Factors in Foreign Exchange📉🔄(What Increases the Supply of a Currency?)
2.1 Central Bank Monetary PolicyðŸ¦(Money Supply & Interest Rate Adjustments)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Central bankscontrol currency supplythrough interest rates and money printing.
Loose monetary policy (low rates, quantitative easing)increases money supply, depreciating currency.
💡Example:
TheEuropean Central Bank (ECB) lowered interest ratesand introduced stimulus packages, increasing thesupply of Euros (EUR).
TheBank of Japan’s low-interest ratesincreased thesupply of Japanese Yen (JPY), making it weaker.
📌Key Takeaway:More money supply weakens a currency, while tight monetary policy strengthens it.
2.2 Government Debt & Fiscal Policy💰(Higher Debt Increases Currency Supply)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Countries withhigh national debtmay increase money supply to cover obligations.
High debt reduces investor confidence, increasing supply as investors sell off the currency.
💡Example:
TheUS dollar saw increased supplyduring the 2008 financial crisis due to stimulus packages.
Argentina’s peso weakenedas government debt rose, increasing peso supply in markets.
📌Key Takeaway:High government debt can lead to more currency supply and depreciation.
2.3 Foreign Exchange Reserves & Currency Intervention🔄(Central Banks Selling Currency to Manage Value)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Central banks buy/sell their currency tostabilize exchange rates.
Selling reservesincreases currency supply, reducing its value.
💡Example:
China’s central bank occasionally sells Yuan (CNY)to keep it competitive in global markets.
Switzerland’s central bank has intervened to weaken the Swiss Franc (CHF)to support exports.
📌Key Takeaway:Governments manipulate currency supply to stabilize economic conditions.
2.4 Import Demand & Trade Deficits🚢(More Imports Increase Currency Supply)
✅Why It Affects Supply?
Atrade deficit(imports > exports) increases supply of local currency in global markets.
Importers exchange local currency for foreign currency, increasing supply.
💡Example:
The US has a persistent trade deficit, increasing thesupply of US dollars in foreign exchange markets.
The UK’s reliance on importshas contributed to GBP fluctuations.
📌Key Takeaway:Countries withtrade deficits see higher currency supply, leading to depreciation.
3. Interaction of Supply & Demand in Foreign Exchange Markets
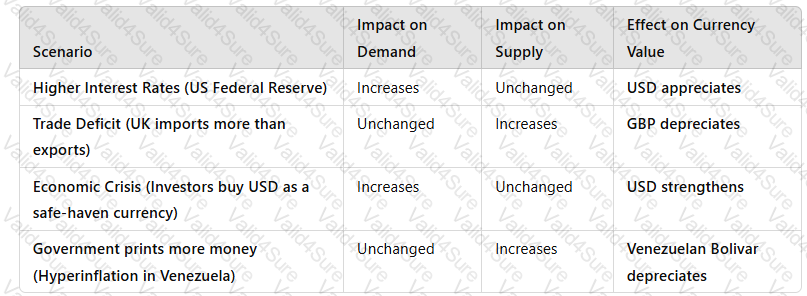 A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
A white grid with black text
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Exchange rates fluctuate based on thebalance between supply and demand.
4. Conclusion
The foreign exchange market operates based onsupply and demand dynamics, influenced by:
✅Demand Factors:
Interest Rates & Inflation– Higher rates strengthen demand.
Trade Balances– Export-driven economies see strong demand.
Investor Sentiment– Economic stability attracts investors.
✅Supply Factors:
Central Bank Policies– Money printing increases supply.
Government Debt– High debt increases supply, lowering value.
Trade Deficits– Import-heavy economies see currency depreciation.
Understanding these factors helps businesses and policymakersmanage foreign exchange risks and optimize international trade strategies.
Assess benchmarking as an approach to analysing an organisations performance.
Answer:
Explanation:
Benchmarking as an Approach to Analyzing Organizational Performance
Introduction
Benchmarking is aperformance measurement toolused by organizations tocompare their processes, products, or servicesagainst industry standards, competitors, or best practices. It helps organizationsidentify performance gaps, set improvement targets, and enhance competitive advantage.
There are different types of benchmarking, includinginternal, competitive, functional, and generic benchmarking, each serving different strategic objectives.
1. Types of Benchmarking
Organizations can adopt different benchmarking approaches based on their goals:
 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
2. How Benchmarking Helps in Performance Analysis
Benchmarking providesquantifiable insightsto assess and improve organizational performance in key areas:
✅Identifies Performance Gaps– Highlights areas where an organization lags behind competitors or industry best practices.✅Improves Operational Efficiency– Helps streamlinesupply chain, production, and customer service processes.✅Enhances Strategic Decision-Making– Supports data-driven decisions forresource allocation, pricing strategies, and process optimization.✅Drives Continuous Improvement– Encourages a culture ofinnovation and best practice adoption.✅Boosts Competitive Advantage– Enables organizations to stay ahead in their market by implementing superior processes.
💡Example:Aretail chain benchmarking delivery speed against Amazonmay adoptAI-driven inventory managementto reduce delays.
3. Advantages of Benchmarking
✅Objective Performance Measurement– Uses industry data to providerealistic performance targets.✅Encourages Best Practice Adoption– Helps companieslearn from successful competitors.✅Enhances Cost Efficiency– Identifiesareas for cost reduction and resource optimization.✅Facilitates Strategic Growth– Helps companies improvecustomer experience, product innovation, and market positioning.
💡Example:McDonald's benchmarked Starbucks' digital loyalty program, leading to the launch ofMyMcDonald’s Rewards, improving customer retention.
4. Limitations of Benchmarking
âŒLimited to Available Data–Confidential industry datamay not always be accessible.âŒLack of Context– Differences inbusiness models, resources, and market conditionscanmake direct comparisons misleading.âŒFocus on Imitation Over Innovation– Firms may focus too much oncopying competitorsrather than developing unique strategies.âŒResource-Intensive– Conducting in-depth benchmarking requirestime, expertise, and financial investment.
💡Example:XYZ Construction benchmarking against a large multinationalmay find certain strategies unrealistic due toscale differences.
5. Application of Benchmarking in Different Sectors
Organizations across industries use benchmarking for performance analysis:
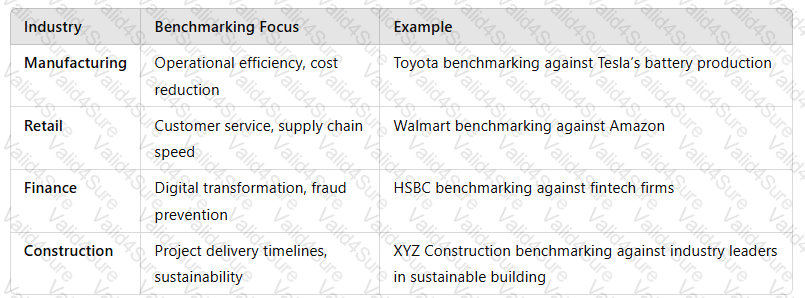 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
Benchmarking is aneffective performance analysis toolthat helps organizationsidentify gaps, adopt best practices, and enhance competitiveness. However, it must be used carefully toavoid blind imitation and consider contextual differences. When integrated with other strategic models (e.g., SWOT, Balanced Scorecard), benchmarking provides apowerful framework for continuous improvement and strategic growth.