P2 Exam Dumps - Advanced Management Accounting
Searching for workable clues to ace the CIMA P2 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s P2 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
A company uses activity based costing. The total production overheads of $16,050 for the next period are for set up costs of $6,450 and quality inspection costs of $9,600. The company produces two products, Product F and Product G. Details relating to the next period are as follows:
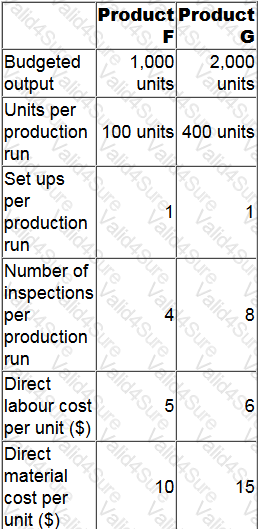
A new customer has offered to purchase Product F for $28.00 per unit. The only costs incurred would be those shown above.
What is the profit per unit of Product F that would be gained by accepting the offer? Give your answer to two decimal places.
An 80% learning curve will apply to the production of a new product. The first unit will require 120 labor hours. The labor rate is $11 per hour.
To the nearest $1, the expected total labor cost for the first 4 units is:
Which THREE of the following are advantages of changing from a 'top-down' to a 'bottom-up' (participative) style of budgeting?
For a pharmaceutical manufacturer, in which perspective of the Balanced Scorecard should the performance measure 'number of patents granted during the year' be included?
We have 2 divisions with the following information: Profit before depreciation: B1=$800,000, B2=S1,000,000; Assets: B1 =$2,000,000, B2=S3,000,000; Capital employed: B1 = $1,700,000 and B2 = $2,550,000. 20%
straight-line depreciation is used.
Calculate ROI for each division.