CTFL-Foundation Exam Dumps - ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level
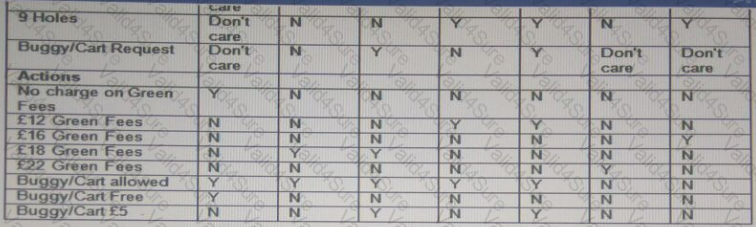
The decision table above reflects a golf club's pricing structure for green fees and buggy/cart hire.
What is the expected result (actions) for each of the following two test cases (TC1 and TC2)?
* TC 1 - Paul is not a full member, is a Loyalty Card holder and requests to play 18 holes with a buggy/cart
* TC 2 - Cheryl is not at full member, doesn't have a Loyalty Card and requests to play 9 holes with a buggy/cart
Which of the following options explain why it is often beneficial to have an independent test function in an organisation?
During the development of a software change for a system, the developer makes a mistake in his work, which leads to a fault in the code. Unfortunately the fault is not found by software testing and is released into live.
What is the definite consequence of this mistake?
Your task is to compile a test execution schedule for the current release of software.
The system specification states the following logical dependencies:
• An admin user must create/amend/delete a standard user.
• A standard user is necessary to perform all other actions.
The test plan requires that re-tests must be performed first, followed by the highest priority tests. To save time, the test plan states that tests should be scheduled to create test data for the subsequent tests in the schedule.
The following test cases have been designed, with an indication of priority (1 being the highest priority) and whether the test has previously failed.
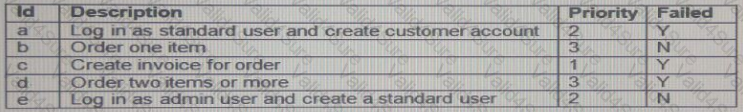
Which test execution schedule meets the test plan requirements and logical dependencies?
Which of the following would achieve the HIGHEST level of testing independence for a project's test level?
Which of the following does NOT represent one of the three triggers for maintenance testing an operational system?
Which of the following optionsBESTexplain the pesticide paradox principle of testing?