ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor Exam Dumps - QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam
An audit team of three people is conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 of an engineering organisation which manufactures sacrificial anodes for the
oil and gas industry in marine environments. These are aluminium products designed to prevent corrosion of submerged steel structures. As one of
the auditors, you find that the organisation has shipped anodes for Project DK in the Gulf of Mexico before the galvanic efficiency test results for the
anodes have been fully analysed and reported as required by the customer. The Quality Manager explains that the Managing Director authorised the
release of the anodes to avoid late delivery as penalties would be imposed. The customer was not informed since the tests rarely fall below the
required efficiency. You raise a nonconformity against clause 8.6 of ISO 9001.
During the audit team meeting in preparation for the Closing meeting, the second auditor disagreed with the clause of ISO 9001 selected for the
above nonconformity. He thinks it should be clause 9.1.1.
Choose three options for how the audit team leader should best respond to the situation:
You are carrying out an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation manufactures cosmetics for major retailers.
You are interviewing the Manufacturing Manager (MM).
You: "I would like to begin by looking at the cleaning controls."
MM: "We record the cleaning of the equipment at the end of every batch. This document details the minimum cleaning frequency and the procedures to follow for all areas and each item of equipment. The person who carries out the cleaning puts their initial on the document and records the time and date alongside."
Narrative: You sample production records over 3-days and note down evidence of nonconformity as per the table below.
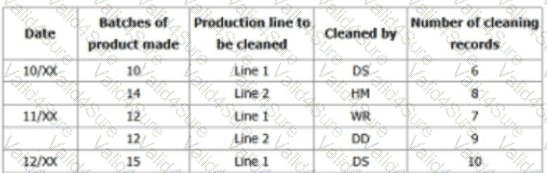
You decide to raise a non-conformity.

You are conducting a Stage 1 audit at an organisation that services refrigeration equipment for a large customer base.
The scope of certification is "Provision of refrigeration equipment maintenance and repair services". You are interviewing
the Managing Director to learn more about the organisation and to explore how the requirements for policy, objectives,
and risks and opportunities in ISO 9001 are addressed.
The Managing Director explains that they only use sub-contract refrigeration engineers and do not have any full-time
refrigeration engineers, which helps to optimise overhead costs. The full-time staff employed are essentially a small team
of office staff who process customer enquiries, schedule jobs and process invoices.
The Managing Director adds that the ISO 9001 requirements for competence of personnel extends to both sub-contract
and full-time staff. He also states that the full-time staff are aware of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address
risk and opportunities.
You ask if the sub-contract engineers have been informed of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address risks and
opportunities, to which the Managing Director replies that this is not applicable as they only use sub-contractors who
operate ISO 9001 certificated quality management systems. The documented information provided to the auditor
confirms this.
Which clause in ISO 9001 is most likely not to have been fulfilled in this instance?
Scenario 6: Davis Clinic (DC) is an American medical center focused on integrated health care. Since its establishment DC was committed to providing qualitative services for its clients, which is the reason why the company decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After a year of having an active QMS in place, DC applied for a certification audit.
A team of five auditors, from a well-known certification body, was selected to conduct the audit. Eva was appointed as the audit team leader. After three days of auditing, the team gathered to review and examine their findings. They also discussed the audit findings with DC's top management and then drafted the audit conclusions.
In the closing meeting, which was held between the audit team and the top management of DC. Eva presented two nonconformities that were detected during the audit. Eva stated that the company did not retain documented information regarding its outsourced services for an analysis laboratory and regarding the conducted management reviews. During the closing meeting, the audit team required from DCs top management to come up with corrective action plans within two weeks. Although the top management did not agree with the audit findings, the audit team insisted that the auditee must submit corrective actions within the given time frame in order for the audit activities to continue.
Once the action plans were evaluated, the audit team began preparing the audit report. Eva required from the team to provide accurate descriptions of the audit findings and the audit conclusions. The report was then distributed to all the interested parties involved in the audit, including the certification body Based on the report, the certification body together with Eva, as the audit team leader, made the certification decision.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Is it acceptable for the certification body and Eva to make the certification decision together?
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
The quality policy was established by Leslie and approved by top management. Is this acceptable? Please refer to scenario 2.
Scenario 7: POLKA is a car manufacturing company based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company has around 14,000 employees working in different sectors which help with the design, painting, assembling, and test drives of the final product. The company is widely known for its qualitative products and affordable prices. In order to retain their reputation, POLKA implemented a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001.
Before applying for certification, the company decided to conduct an internal audit to check whether there are any nonconformities in their QMS and if the requirements of ISO 9001 are being fulfilled. The top management appointed Sean, the internal auditor, as the team leader of the internal audit team. Sean required from the top management to have unrestricted access to the employees and executives of POLKA and to the documented information. Furthermore, Sean required to establish a team with a large number of auditors, considering the size and the complexity of the organization. The top management of POLKA agreed with Sean's requirements.
The top management, in cooperation with Sean, assigned 10 more employees to the audit team. Following that. Sean planned the audit activities and assigned the roles and responsibilities to each auditor. They began by interviewing employees of different manufacturing departments to check whether they are aware of the process of the QMS implementation. While conducting these activities, one of the auditors asked Sean for permission to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis, as he was very familiar with the processes of the department.
Along the way, the teams findings showed that the staff were trained, documented information was updated, and the QMS fulfilled the requirements of ISO 9001. The internal audit took three weeks to complete, and on the last week the audit team held a final meeting
The team shared their results and together drafted the audit report This report was submitted to the top management of the company. The report was maintained as documented information, and was available to the relevant interested parties.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
According to Scenario 7, one of the auditors requested permission from Sean to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis. Should Sean grant the auditor permission?
Even though past audits have highlighted a consistently large number of nonconformities within an organisation's design team, the organisation has not varied the frequency or duration of audits on its audit plan.
The decision for whether this situation is acceptable or not should be governed by which of the following?
State the correct sequence of events in the certification process for an organisation to obtain third-party accredited certification to ISO 9001.
