P1 Exam Dumps - Management Accounting
Searching for workable clues to ace the CIMA P1 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s P1 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
Traditional absorption costing is more suitable than activity-based costing when:
Which of the following are examples of feedforward control?
Select ALL that apply.
A company produces three products D, E and F. The statement below shows the selling price and product costs per unit for each product, based on a traditional absorption costing system.
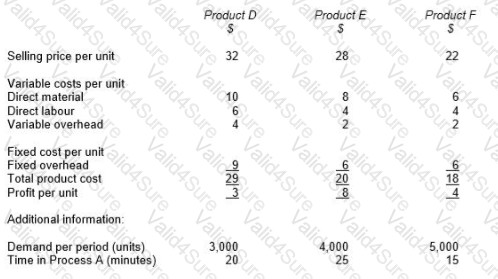
Each of the products is produced using Process A which has a maximum capacity of 2,500 hours per period.
If a traditional contribution approach is used, the ranking of products, in order of priority, for the profit maximizing product mix will be:
Company XPP sells a perishable product that has to be produced each day in anticipation of the following day's sales.
Any product remaining unsold at the end of the day following production is wasted.
The payoff table below shows the daily profit or loss depending on the amounts produced and sold.
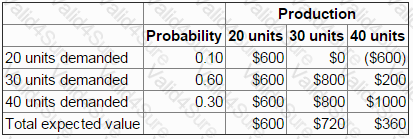
A new ordering system is being discussed with customers.
The new system would require customers to order in advance to enable production each day of the following day's sales quantity, thus eliminating waste.
What is the expected increase in average daily profit if the new system is accepted by customers?
Give your answer as a whole number.
Place the correct label against each item to categorise the cost of the item within the quality cost framework.

A snowboard manufacturer is considering investing in technology that will give a good indication of how heavy snowfall will be in the future. The predictions tend to be reasonably accurate.
The current budgeted profit for the year is £2,560,000 but if they invest in this technology and it works, the expected profit will be £2,640,000. The manufacturer is willing to invest a maximum of £40,000 into the venture.
What is the expected profit if the investment is NOT made?

Select the benefits to a company of using sensitivity analysis in investment appraisal.
(Select all the true statements.)